| Target Namespace | http://www.isan.org/schema/v1.1/common/language |
|---|---|
| Version | 1.1 |
| Element and Attribute Namespaces |
|
| Schema Composition |
|
| Prefix | Namespace |
|---|---|
| Default namespace | http://www.isan.org/schema/v1.1/common/language |
| xml | http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace |
| xs | http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema |
| Super-types: | None |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
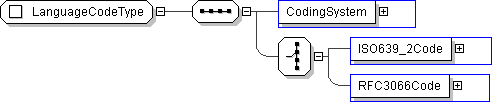
| Name | LanguageCodeType |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Complex Type LanguageType |
| Abstract | no |

| Super-types: | None |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | LanguageType |
|---|---|
| Abstract | no |
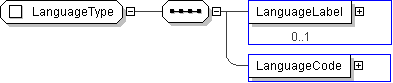
| Super-types: | xs:string < CodingSystemType (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
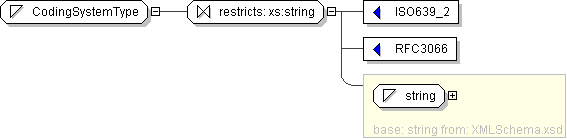
| Name | CodingSystemType |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Complex Type LanguageCodeType |
| Content |
|
| Super-types: | xs:string < ISO639_2CodeType (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | ISO639_2CodeType |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Complex Type LanguageCodeType |
| Content |
|
| Documentation | ABK : Abkhazian ACE : Achinese (Aceh) ACH : Acoli ADA : Adangme (One of the Ghana language) AAR : Afar AFH : Afrihili AFR : Afrikaans AFA : Afro-Asiatic (Other) AKA : Akan (One of the Ghana language) AKK : Akkadian (Babylonian) ALB : Albanian ALE : Aleut (an Eskimo language from Aleutian Islands) ALG : Algonquian languages TUT : Altaic (Other) AMH : Amharic (or Abyssinian, main language of Ethiopia) APA : Apache languages ARA : Arabic ARC : Aramaic (Syria) ARP : Arapaho ARN : Araucanian (S. Central Chile) ARW : Arawak ARM : Armenian (Hayeren) ART : Artificial (Other) ASM : Assamese (Indo-Iranian subfamily) ATH : Athapascan languages AUS : Australian languages MAP : Austronesian (Other, Malayo-Polynesian) AVA : Avaric AVE : Avestan AWA : Awadhi AYM : Aymara (language from indigenous people near lake Titicaca basin in Peru and Bolivia) AZE : Azerbaijani (Azeri) NAH : Aztec (Nahuatl) BAN : Balinese BAT : Baltic (Other) BAL : Baluchi BAM : Bambara BAI : Bamileke languages BAD : Banda BNT : Bantu (Other) BAS : Basa BAK : Bashkir BAQ : Basque BTK : Batak (Indonesia) BEJ : Beja (spoken near Ethiopia and ajoining regions) BEL : Belarussian (white russian) BEM : Bemba BEN : Bengali (Bangla) BER : Berber (Other) BHO : Bhojpuri BIH : Bihari (an east indic language) BIK : Bikol BIN : Bini BIS : Bislama (one of the major Vanuatu language) BRA : Braj BRE : Breton (Brez) BUG : Buginese (Bugi) BUL : Bulgarian BUA : Buriat BUR : Burmese (Myanmasa) (belonging to the Tibeto-Burman subfamily) CAD : Caddo XCA : Cantonese (Chinese dialect from Guangzhou) CAR : Carib XCS : Caspian CAT : Catalan CAU : Caucasian (Other) CEB : Cebuano CEL : Celtic (Other) CAI : Central American Indian (Oth.) XCH : Chadic (spoken in Chad, northern Cameroon and northern Nigeria) CHG : Chagatai CMC : Chamic languages CHA : Chamorro (Guam and Northern Mariana Islands) CHE : Chechen CHR : Cherokee CHY : Cheyenne CHB : Chibcha (Colombia) CHI : Chinese (Zhongwen) CHN : Chinook jargon CHP : Chipewyan CHO : Choctaw CHU : Church Slavic CHK : Chuukese CHV : Chuvash COP : Coptic COR : Cornish COS : Corsican CRE : Cree MUS : Creek (Muskogee) CRP : Creoles and pidgins (Other) CPE : Creoles and pidgins, English-based (Other) CPF : Creoles and pidgins, French-based (Other) CPP : Creoles and pidgins, Portuguese-based (Other) SCR : Croatian CUS : Cushitic (Other) CZE : Czech DAK : Dakota DAN : Danish DAY : Dayak DEL : Delaware DIN : Dinka DIV : Divehi (Maldives) DOI : Dogri DGR : Dogrib DRA : Dravidian (Other) DUA : Duala DUT : Dutch DUM : Dutch, Middle (ca. 1050-1350) DYU : Dyula DZO : Dzongkha (=Bhutani) EFI : Efik EGY : Egyptian (Ancient) EKA : Ekajuk ELX : Elamite ENG : English ENM : English, Middle (1100-1500) ANG : English, Old (ca. 450-1100) EPO : Esperanto EST : Estonian (Eesti) EWE : Ewe (main language of Togo) EWO : Ewondo FAN : Fang (Equatorial Guinea and Gabon) FAT : Fanti (One of the Ghana language) FAO : Faroese (Faeroese Island) FIJ : Fijian FIN : Finnish (Suomi) FIU : Finno-Ugrian (Lapland language) FON : Fon (Official language of Benin with French) FRE : French FRM : French, Middle (ca. 1400-1600) FRO : French, Old (ca. 842-1400) FRY : Frisian (Frysk) FUR : Friulian FUL : Fulah (From Senegal to eastern Sudan) GAA : Ga GLA : Gaelic (Scots) GLG : Gallegan (Galician, Galego) LUG : Ganda (or Baganda, Uganda) GAY : Gayo GBA : Gbaya GEZ : Geez (classical Ethiopic) GEO : Georgian (Kartuli) GER : German GMH : German, Middle High (ca. 1050-1500) GOH : German, Old High (ca. 750-1050) GEM : Germanic (Other) GIL : Gilbertese (Kiribati) GON : Gondi GOR : Gorontalo GOT : Gothic GRB : Grebo GRC : Greek, Ancient (to 1453) GRE : Greek, Modern (1453-) (Ellinika) GRN : Guarani (bolivia, paraguay, and south of Brezil) GUJ : Gujarati (northwest india) GWI : Gwich'in HAI : Haida HAU : Hausa (Nigeria) HAW : Hawaiian HEB : Hebrew (Iwrith) HER : Herero (Namibia) HIL : Hiligaynon HIM : Himachali HIN : Hindi (official language of northern India) HMO : Hiri Motu HIT : Hittite HMN : Hmong HUN : Hungarian (Magyar) HUP : Hupa IBA : Iban ICE : Icelandic IBO : Igbo IJO : Ijo ILO : Iloko INC : Indic (Other) INE : Indo-European (Other) IND : Indonesian INA : Interlingua (International Auxilary Language Association) ILE : Interlingue IKU : Inuktitut IPK : Inupiak IRA : Iranian (Other) GLE : Irish MGA : Irish, Middle (900-1200) SGA : Irish, Old (to 900) IRO : Iroquoian languages ITA : Italian JPN : Japanese (Nihongo) JAV : Javanese JRB : Judeo-Arabic JPR : Judeo-Persian KAB : Kabyle KAC : Kachin KAL : Kalaallisut (or Greenlandic) KAM : Kamba (Kenya) KAN : Kannada KAU : Kanuri KAA : Kara-Kalpak KAR : Karen KAS : Kashmiri KAW : Kawi KAZ : Kazakh KHA : Khasi KHM : Khmer (Cambodian) KHI : Khoisan (Other) (Namibia and West South Africa) KHO : Khotanese (or Saka, East Iranian) KIK : Kikuyu (Northern Kenya) KMB : Kimbundu (Angola) KIN : Kinyarwanda (Rwanda) KIR : Kirghiz KOM : Komi KON : Kongo KOK : Konkani (south indic) KOR : Korean KOS : Kosraean KPE : Kpelle KRO : Kru KUA : Kuanyama KUM : Kumyk KUR : Kurdish KRU : Kurukh KUT : Kutenai LAD : Ladino LAH : Lahnda LAM : Lamba LAO : Lao (= Laothian) LAT : Latin LAV : Latvian (= lettish, letonian) XLA : Laz LTZ : Letzeburgesch (luxembourg low german dialect) LEZ : Lezghian LIN : Lingala LIT : Lithuanian LOZ : Lozi LUB : Luba-Katanga LUA : Luba-Lulua (Central Zaire) LUI : Luiseno LUN : Lunda LUO : Luo (Kenya and Tanzania) LUS : Lushai MAC : Macedonian MAD : Madurese MAG : Magahi MAI : Maithili MAK : Makasar MLG : Malagasy MAY : Malay MAL : Malayalam MLT : Maltese MDR : Mandar XAA : Mandarin dialect MAN : Mandingo (spoken in Sierra Leone, Liberia, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Mali and Burkina Faso) MNI : Manipuri MNO : Manobo languages GLV : Manx MAO : Maori MAR : Marathi CHM : Mari MAH : Marshall MWR : Marwari MAS : Masai (Nomadic people of East Africa, Kenya and Tanzania) MYN : Mayan languages MEN : Mende (Sierra Leone) MIC : Micmac MIN : Minangkabau MIS : Miscellaneous languages MOH : Mohawk MOL : Moldavian MKH : Mon-Khmer (Other) LOL : Mongo MON : Mongolian MOS : Mossi (More) MUL : Multiple languages MUN : Munda languages XMU : Mute film NAU : Nauru NAV : Navajo NDE : Ndebele, North (Zimbabwe, Botswana) NBL : Ndebele, South (Zimbabwe, Botswana) NDO : Ndonga NEP : Nepali NEW : Newari NIA : Nias NIC : Niger-Kordofanian (Other) SSA : Nilo-Saharan (Other) NIU : Niuean (Niue Island) NON : Norse, Old NAI : North American Indian (Other) NOR : Norwegian NUB : Nubian languages NYM : Nyamwezi NYA : Nyanja NYN : Nyankole NYO : Nyoro NZI : Nzima OCI : Occitan (post 1500) OJI : Ojibwa ORI : Oriya ORM : Oromo (Galla or Afan) (West and South Ethiopia and Kenya) OSA : Osage OSS : Ossetic OTO : Otomian languages PAL : Pahlavi PAU : Palauan (Palau Island in Micronesia) PLI : Pali PAM : Pampanga PAG : Pangasinan PAN : Panjabi (language of Punjab) PAP : Papiamento PAA : Papuan (Other) PER : Persian (=Farsi) PEO : Persian, Old (ca. 600-400 B.C.) PHI : Philippine (Other) PHN : Phoenician PON : Pohnpeian POL : Polish POR : Portuguese PRA : Prakrit languages PRO : Provencal, Old (to 1500) PUS : Pushto (or Pachto, Afghan) XPY : Pygmies language QUE : Quechua (Bolivia, Peru and Ecuador) ROH : Raeto-Romance RAJ : Rajasthani RAP : Rapanui RAR : Rarotongan ROA : Romance (Other) RUM : Romanian ROM : Romany (Gipsy language) RUN : Rundi (or Kirundi) RUS : Russian SAL : Salishan languages SAM : Samaritan Aramaic SMI : Sami languages SMO : Samoan SAD : Sandawe SAG : Sango (Central African Republic) SAN : Sanskrit SAT : Santali SRD : Sardinian SAS : Sasak SCO : Scots SEL : Selkup SEM : Semitic (Other) SCC : Serbian SRR : Serer SHN : Shan SNA : Shona SID : Sidamo BLA : Siksika (Blackfoot) SND : Sindhi SIN : Sinhalese (Sri Lanka) SIT : Sino-Tibetan (Other) SIO : Siouan languages DEN : Slave (Athapascan) SLA : Slavic (Other) SLO : Slovak SLV : Slovenian SOG : Sogdian NSO : Sohto, Northern SOM : Somali SON : Songhai SNK : Soninke WEN : Sorbian languages SOT : Sotho (Southern, language of the Lesotho) SAI : South American Indian (Other) SPA : Spanish SUK : Sukuma SUX : Sumerian SUN : Sundanese SUS : Susu (Guinea) SWA : Swahili (a bantu language over much of east Africa and the Congo region) SSW : Swati (= Siswant, Siswati) SWE : Swedish XCD : Swiss German dialect XCI : Swiss Italian dialect SYR : Syriac TGL : Tagalog (Philipines) TAH : Tahitian TAI : Tai (Other) TGK : Tajik TMH : Tamashek TAM : Tamil (part of India and Sri Lanka) TAT : Tatar TEL : Telugu TER : Tereno TET : Tetum THA : Thai TIB : Tibetan (Bodskad) TIG : Tigre TIR : Tigrinya TEM : Timne TIV : Tiv TLI : Tlingit TPI : Tok Pisin TKL : Tokelau TOG : Tonga (Nyasa) TON : Tonga (Tonga Islands) TSI : Tsimshian TSO : Tsonga TSN : Tswana (= Setswana) TUM : Tumbuka TUR : Turkish OTA : Turkish, Ottoman (1500-1928) TUK : Turkmen TVL : Tuvalu TYV : Tuvinian TWI : Twi ZZZ : UNKNOWN UGA : Ugaritic UIG : Uighur UKR : Ukrainian UMB : Umbundu URD : Urdu (=Pakistanian) UZB : Uzbek VAI : Vai VEN : Venda (South africa) VIE : Vietnamese VOL : Volapuk VOT : Votic WAK : Wakashan languages WAL : Walamo XWA : Wallon WAR : Waray WAS : Washo WEL : Welsh WOL : Wolof (niger-congo language of senegambia) XHO : Xhosa (Lesotho, Bantustan, South Africa) SAH : Yakut YAO : Yao YAP : Yapese YID : Yiddish YOR : Yoruba (South West Nigeria and Benin) YPK : Yupik languages ZND : Zande ZAP : Zapotec ZEN : Zenaga ZHA : Zhuang ZUL : Zulu ZUN : Zuni |

| Super-types: | xs:string < LanguageLabelType (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | LanguageLabelType |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Complex Type LanguageType |
| Content |
|

| Super-types: | xs:string < RFC3066CodeType (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | RFC3066CodeType |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Complex Type LanguageCodeType |
| Content |
|
| Documentation | aa : Afar ab : Abkhazian ace : Achinese ach : Acoli ada : Adangme ady : Adygei/Adyghe ae : Avestan af : Afrikaans afa : Afro-Asiatic (Other) afh : Afrihili ain : Ainu ak : Akan akk : Akkadian ale : Aleut alg : Algonquian languages am : Amharic an : Aragonese ang : English, Old (ca.450-1100) apa : Apache languages ar : Arabic arc : Aramaic arn : Araucanian arp : Arapaho art : Artificial (Other) arw : Arawak as : Assamese ast : Asturian; Bable ath : Athapascan languages aus : Australian languages av : Avaric awa: Awadhi ay : Aymara az : Azerbaijian/Azeri az-Cyrl : Azerbaijian/Azeri (Cyrillic script) az-Latn : Azerbaijian/Azeri (Latin script) ba : Bashkir bad: Banda bai : Bamileke languages bal : Baluchi ban : Balinese bas : Basa bat : Baltic (Other) be : Belarusian bej : Beja bem: Bemba ber : Berber (Other) bg : Bulgarian bh : Bihari bho: Bhojpuri bi : Bislama bik : Bikol bin : Bini bla : Siksika bm : Bambara bn : Bengali/Bangla bnt : Bantu (Other) bo : Tibetan br : Breton bra : Braj bs : Bosnian bs-Cyrl : Bosnian (Cyrillic script) bs-Latn : Bosnian (Latin script) btk : Batak (Indonesia) bua : Buriat bug: Buginese byn : Bilin ca : Catalan/Valencian cad : Caddo cai : Central American Indian (Other) car : Carib cau : Caucasian (Other) ce : Chechen ceb: Cebuano cel : Celtic (Other) ch : Chamorro chb : Chibcha chg : Chagatai chk : Chuukese chm: Mari chn : Chinook Jargon cho : Choctaw chp : Chipewyan chr : Cherokee chy : Cheyenne cmc: Chamic languages co : Corsican cop: Coptic cpe: Creoles and pidgins, English-based (Other) cpf : Creoles and pidgins, French-based (Other) cpp: Creoles and pidgins, Portuguese-based (Other) cr : Cree crh : Crimean Tatar/Crimean Turkish crp : Creoles and Pidgins (Other) cs : Czech csb : Kashubian cu : Church Slavic/Old Slavonic/Old Bulgarian cus : Cushitic (Other) cv : Chuvash cy : Welsh da : Danish dak : Dakota dar : Dargwa day : Dayak de : German del : Delaware den: Slave (Athapascan) dgr : Dogrib din : Dinka doi : Dogri dra : Dravidian (Other) dsb: Lower Sorbian dua : Duala dum: Dutch, Middle (ca.1050-1350) dv : Divehi dyu : Dyula dz : Dzongkha/Bhutani ee : Ewe efi : Efik egy : Egyptian (Ancient) eka : Ekajuk el : Greek elx : Elamite en : English en-GB : English, UK enm : English, Middle (1100-1500) en-US : English, US eo : Esperanto es : Spanish es-419 : Spanish, Latin American es-AR : Spanish, Argentinian es-CL : Spanish, Chilean es-ES : Spanish, Castilian es-MX : Spanish, Mexican es-PR : Spanish, Puerto Rican et : Estonian eu : Basque ewo: Ewondo fa : Persian/Farsi fan : Fang fat : Fanti ff : Fulah fi : Finnish fil : Filipino/Pilipino fiu : Finno-Ugrian (Other) fj : Fijian fo : Faroese fon : Fon fr : French fr-CA: French, Canadian fr-FR: French, Parisian frm : French, Middle (ca.1400-1800) fro : French, Old (842-ca.1400) fur : Friulian fy : Frisian ga : Gaelic (Irish) gaa : Ga gay : Gayo gba: Gbaya gd : Gaelic (Scottish) gem: Germanic (Other) gez : Geez gil : Gilbertese gl : Galician gmh: German, Middle High (ca.1050-1500) gn : Guarani goh: German, Old High (ca. 750-1050) gon: Gondi gor : Gorontalo got : Gothic grb : Grebo grc : Greek, Ancient (to 1453) gsw-AT: German, Austrian/Alemannisch gsw-CH: German, Swiss/ Schwyzerdütsch gu : Gujarati gv : Manx gwi : Gwich´in ha : Hausa hai : Haida haw: Hawaiian he : Hebrew hi : Hindi hil : Hiligaynon him : Himachali hit : Hittite hmn: Hmong ho : Hiri Motu hr : Croatian hsb : Upper Sorbian ht : Haitian/Haitian Creole hu : Hungarian hup : Hupa hy : Armenian hz : Herero ia : Interlingua (International Auxiliary Language Association) iba : Iban id : Indonesian ie : Interlingue ig : Igbo ii : Sichuan Yi ijo : Ijo ik : Inupiaq ilo : Iloko inc : Indic (Other) ine : Indo-European (Other) inh : Ingush io : Ido ira : Iranian (Other) iro : Iroquoian languages is : Icelandic it : Italian it-CH: Italian, Swiss iu : Inuktitut ja : Japanese jbo : Lojban jpr : Judeo-Persian jrb : Judeo-Arabic jv : Javanese ka : Georgian (Kartuli) kaa : Kara-Kalpak kab : Kabyle kac : Kachin kam: Kamba kar : Karen kaw: Kawi kbd : Kabardian kg : Kongo kha : Khasi khi : Khoisan (Other) kho : Khotanese ki : Kikuyu/Gikuyu kj : Kuanyama/Kwanyama kk : Kazakh kl : Kalaallisut/Greenlandic km : Khmer kmb: Kimbundu kn : Kannada ko : Korean kok : Konkani kos : Kosraean kpe : Kpelle kr : Kanuri krc : Karachay-Balkar kro : Kru kru : Kurukh ks : Kashmiri ku : Kurdish kum: Kumyk kut : Kutenai kv : Komi kw : Cornish ky : Kirghiz la : Latin lad : Ladino lah : Lahnda lam : Lamba lb : Letzeburgesch/Luxembourgish lez : Lezghian lg : Ganda li : Limburgan/Limburger/Limburgish ln : Lingala lo : Lao lol : Mongo loz : Lozi lt : Lithuanian lu : Luba-Katanga lua : Luba-Lulua lui : Luiseno lun : Lunda luo : Luo (Kenya and Tanzania) lus : Lushai lv : Latvian mad: Madurese mag: Magahi mai : Maithili mak: Makasar man: Mandingo map: Austronesian (Other) mas: Masai mdf: Moksha mdr: Mandar men: Mende mg : Malagasy mga: Irish, Middle (900-1200) mh : Marshallese mi : Maori mic : Micmac min : Minangkabau mis : Miscellaneous mk : Macedonian mkh: Mon-Khmer (Other) ml : Malayalam mn : Mongolian mnc: Manchu mni : Manipuri mno: Manobo languages mo : Moldavian moh: Mohawk mos: Mossi (Moré) mr : Marathi ms : Malay mt : Maltese mul : Multiple languages mun: Munda languages mus: Creek mwl: Mirandese mwr: Marwari my : Burmese myn: Mayan languages myv: Erzya na : Nauru nah : Nahuatl nai : North American Indian (Other) nap : Neapolitan nb : Norwegian Bokmål nd : Ndebele, North nds : German, Low/Saxon, Low ne : Nepali new: Newari/Nepal Bhasa ng : Ndonga nia : Nias nic : Niger-Kordofanian (Other) niu : Niuean nl : Dutch nl-BE: Dutch, Flemish nl-NL: Dutch, Netherlands nn : Norwegian Nynorsk no : Norwegian nog: Nogai non : Norse, Old nr : Ndebele, South nso : Sotho, Northern/Pedi/Sepedi nub : Nubian languages nv : Navajo/Navaho nwc: Classical Nepal Bhasa/Old Newari ny : Chewa/Chichewa/Nyanja nym: Nyamwezi nyn : Nyankole nyo : Nyoro nzi : Nzima oc : Occitan (post 1500)/Provençal oj : Ojibwa om : Oromo or : Oriya os : Ossetian/Ossetic osa : Osage ota : Turkish, Ottoman (1500-1928) oto : Otomian languages pa : Punjabi paa : Papuan (Other) pag: Pangasinan pal : Pahlavi pam: Pampanga pap: Papiamento pau : Palauan peo: Persian, Old (ca.600-400 B.C.) phi : Philippine (Other) phn : Phoenician pi : Pali pl : Polish pon: Pohnpeian pra : Prakrit languages pro : Provençal, Old (to 1500) ps : Afghan/Pushto pt : Portuguese pt-BR: Portuguese, Brazilian pt-PT: Portuguese, Classic qsi : Silent qu : Quechua raj : Rajasthani rap : Rapanui rar : Rarotongan rm : Raeto-Romance rn : Rundi/Kirundi ro : Romanian roa : Romance (Other) rom: Romany ru : Russian rup : Aromanian/Macedo-Romanian rw : Kinyarwanda sa : Sanskrit sad : Sandawe sah : Yakut sai : South American Indian (Other) sal : Salishan Languages sam: Samaritan Aramaic sas : Sasak sat : Santali sc : Sardinian scn : Sicilian sco : Scots sd : Sindhi sd-Arab: Sindhi (Arabic script) sd-Deva: Sindhi (Devangari script) sd-Guru: Sindhi (Gurmukhi script) se : Sami, Northern sel : Selkup sem: Semitic (Other) sg : Sango sga : Irish, Old (to 900) sgn : Sign languages sh : Serbo-Croatian shn : Shan si : Sinhalese sid : Sidamo sio : Siouan languages sit : Sino-Tibetan (Other) sk : Slovak sl : Slovenian sla : Slavic (Other) sm : Samoan smi : Sami languages (Other) smj : Lule Sami smn: Inari Sami sms: Skolt Sami sn : Shona snk : Soninke so : Somali sog: Sogdian son : Songhai sq : Albanian sr : Serbian sr-Cryl : Serbian (Cryillic) sr-Latn : Serbian (Latin) srr : Serer ss : Swati ssa : Nilo-Saharan (Other) st : Sotho, Southern su : Sundanese suk : Sukuma sus : Susu sux : Sumerian sv : Swedish sw : Swahili syr : Syriac ta : Tamil tai : Tai (Other) te : Telugu tem: Timne ter : Tereno tet : Tetum tg : Tajik th : Thai ti : Tigrinya tig : Tigre tiv : Tiv tk : Turkmen tkl : Tokelau tl : Tagalog tlh : Klingon/tlhIngan-Hol tli : Tlingit tmh : Tamashek tn : Tswana to : Tonga (Tonga Islands) tog : Tonga (Nyasa) tpi : Tok Pisin tr : Turkish ts : Tsonga tsi : Tsimshian tt : Tatar tum : Tumbuka tup : Tupi languages tut : Altaic (Other) tvl : Tuvalu tw : Twi ty : Tahitian tyv : Tuvinian udm: Udmurt ug : Uighur/Uyghur uga : Ugaritic uk : Ukrainian umb: Umbundu und : Undetermined ur : Urdu uz : Uzbek vai : Vai ve : Venda vi : Vietnamese vo : Volapük vot : Votic wa : Walloon wak: Wakashan languages wal : Walamo war : Waray was: Washo wen: Sorbian languages wo : Wolof xal : Kalmyk xh : Xhosa yao : Yao yap : Yapese yi : Yiddish yo : Yoruba ypk : Yupik languages za : Zhuang/Chuang zap : Zapotec zen : Zenaga zh : Chinese zh-cmn : Chinese, Mandarin zh-cmn-Hans : Chinese, Mandarin (Simplified script) zh-cmn-Hant : Chinese, Mandarin (Traditional script) zh-min-nan : Taiwanese zh-yue : Chinese, Cantonese znd : Zande zu : Zulu zun : Zuni |

| Super-types: | Address < AusAddress (by extension) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: |
|
| Name | AusAddress |
|---|---|
| Abstract | no |
The XML Instance Representation table above shows the schema component's content as an XML instance.
Abstract (Applies to complex type definitions and element declarations). An abstract element or complex type cannot used to validate an element instance. If there is a reference to an abstract element, only element declarations that can substitute the abstract element can be used to validate the instance. For references to abstract type definitions, only derived types can be used.
All Model Group Child elements can be provided in any order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-all.
Choice Model Group Only one from the list of child elements and model groups can be provided in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-choice.
Collapse Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32). Then, collapse contiguous sequences of space characters into single space character, and remove leading and trailing space characters.
Disallowed Substitutions
(Applies to element declarations). If substitution is specified, then substitution group members cannot be used in place of the given element declaration to validate element instances. If derivation methods, e.g. extension, restriction, are specified, then the given element declaration will not validate element instances that have types derived from the element declaration's type using the specified derivation methods. Normally, element instances can override their declaration's type by specifying an xsi:type attribute.
Key Constraint Like Uniqueness Constraint, but additionally requires that the specified value(s) must be provided. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.
Key Reference Constraint Ensures that the specified value(s) must match value(s) from a Key Constraint or Uniqueness Constraint. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.
Model Group Groups together element content, specifying the order in which the element content can occur and the number of times the group of element content may be repeated. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#Model_Groups.
Nillable
(Applies to element declarations). If an element declaration is nillable, instances can use the xsi:nil attribute. The xsi:nil attribute is the boolean attribute, nil, from the http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance namespace. If an element instance has an xsi:nil attribute set to true, it can be left empty, even though its element declaration may have required content.
Notation A notation is used to identify the format of a piece of data. Values of elements and attributes that are of type, NOTATION, must come from the names of declared notations. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cNotation_Declarations.
Preserve Whitespace Policy Preserve whitespaces exactly as they appear in instances.
Prohibited Derivations (Applies to type definitions). Derivation methods that cannot be used to create sub-types from a given type definition.
Prohibited Substitutions (Applies to complex type definitions). Prevents sub-types that have been derived using the specified derivation methods from validating element instances in place of the given type definition.
Replace Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32).
Sequence Model Group Child elements and model groups must be provided in the specified order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-sequence.
Substitution Group Elements that are members of a substitution group can be used wherever the head element of the substitution group is referenced.
Substitution Group Exclusions (Applies to element declarations). Prohibits element declarations from nominating themselves as being able to substitute a given element declaration, if they have types that are derived from the original element's type using the specified derivation methods.
Target Namespace The target namespace identifies the namespace that components in this schema belongs to. If no target namespace is provided, then the schema components do not belong to any namespace.
Uniqueness Constraint Ensures uniqueness of an element/attribute value, or a combination of values, within a specified scope. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.